Urban Programs in the Philippines: A Snapshot

Urban Programs in the Philippines: A Snapshot
1980s-Now
Urban Programs in the Philippines: In More Detail
1980s-Now
1976 Urban Milestone
Manila once again becomes the capital of the Philippines.

USAID began the Managing Energy and Resource Efficient Cities (MEREC) project to help intermediate-sized urban cities survive energy crunches and manage resources through institutional knowledge exchange. The project was piloted in Tacloban City and was not scaled elsewhere.
1982 Urban Milestone
Barangay elections are held for the first time, solidifying local leadership.

USAID funds the Local Development Assistance Program to assist the Philippine government in decentralization in the hopes of promoting broad-based, sustainable economic growth and infrastructure in rural areas through the partnership of the private and public sectors.
1991 Urban Milestone
The Local Government Code was enacted, which established systems and powers of the local government in the Philippines: provinces, cities, municipalities, and barangays. This gave local officials greater autonomy to use their own resources to deliver public goods and services.

Industrial Environmental Management Project
The Agency worked to prevent or reproduce pollution at its sources, reclaiming industrial wastes and encouraging cost-effective pollution abatement technologies.

General Santos City Area Development Project
This project improved infrastructure by the Makar Wharf, constructed a new airport at Tambler, and encouraged private investments in post-harvest and service facilities in order to optimize the value of agricultural and marine resources such as cash crops, livestock, poultry and fish that are traded in the city by farmers and fisherfolk.
1992 Urban Milestone
The 1992 Urban Development Housing Act is passed, which ensures private sector participation in the national shelter program.

USAID designed this project to achieve effective local governance in selected provinces and independent cities and establish a functioning system of communication to support replication in urban areas. This program came at a time when local government units needed to develop local champions in participatory governance, in response to the Local Government Code of 1991.
2000 Urban Milestone
The Ecological Solid Waste Management Act of 2000 provided an ecological solid waste management program, creating the necessary institutional mechanisms and incentives, declaring certain acts prohibited and providing penalties, and appropriating funds.
2001 Urban Milestone
The National Framework for Physical Planning (2001-2030) is enacted to set policy and planning guidelines for urban development.

Philippines Environmental Governance Project (Eco-Gov)
The Agency supported the Philippine Government in revitalizing the economy through improved management of the environment and natural resources, with an emphasis on Mindanao and focuses on forests, coastal resources and solid wastes. Support activities included improving the legal and administrative policy framework; improving the capacity of local government, judiciary, and other stakeholder groups; and increasing public information and advocacy for environmental issues.

Local Initiatives for Affordable Wastewater Treatment in the Philippines
This project assisted four selected cities (Dumaguete, Iloilo, Muntinlupa, Naga) to develop low-cost wastewater treatment facilities through the promotion and adoption of low-cost sanitation technology and innovative financing solutions.

Further supported improved access to clean water and sanitation for the urban poor in the Philippines, concluding with a city-wide septic management program in Marikina.

Philippine Water Revolving Fund
USAID facilitated a partnership between water utilities and banks that helped institutionalize private financing for water supply and sanitation projects.

Philippine Sanitation Alliance
A four-year program that worked with public and private sector partners to reduce public health risks, protect biodiversity and other natural resources by developing and implementing stakeholder-driven sanitation initiatives and investments. The project increased the capacity of local governments and water districts to address sanitation challenges and increased public awareness and demand for improved sanitation services and willingness to pay user fees.
2009 Urban Milestone
The Climate Change Act of the Philippines of 2009 mandated various levels of governance in order to consider climate change issues in their regular functions.
2010 Urban Milestone
The Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Act of 2010 created a mandatory local disaster risk reduction and management officer in local governments.

Through the Partnership for Growth, USAID collaborated with seven U.S. Government agencies and the Philippine government to address the country’s most binding constraints to lasting, shared growth. The partnership is a “whole-of-government” endeavor to unlock the growth potential of partner countries to become the next generation of emerging markets.

Investment Enabling Environment (INVEST)
The INVEST Project sought to improve local business climate in the Philippines by lowering transaction costs, reducing the cost of doing business in national and local level regulations and processes, and increasing the flow of private investment and business start-ups in the Philippines.

USAID worked to strengthen the economic competitiveness and resilience of second-tier cities, outside of Metro Manila. CDI worked to improve the investment climate in Batangas, Cagayan de Oro and Iloilo by fostering an open and competitive business climate, facilitating investments in high-value industry clusters, enhancing human capital development, strengthening health services, and ensuring urban resilience.

This project worked to increase sustainable access to water and wastewater treatment services and resilience to water stress and extreme weather in the cities of Isabela (Basilan), Iloilo, Tacloban, Cotabato, Cagayan de Oro and Zamboanga.
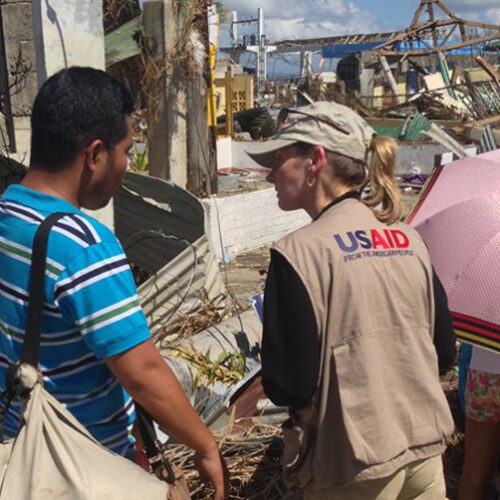

USAID delivered life-saving support, including the provision of emergency shelter, food assistance, relief communities, and water and sanitation support after the Super Typhoon Haiyan made landfall in the Philippines. Afterwards, USAID partnered with Procter & Gamble and Coca-Cola and signed a MOU to support the revival of economic activity and livelihoods by rebuilding sari-sari stores and facilitating owners’ access to microfinancing loans.

The Building Low Emission Alternatives to Develop Economic Resilience and Sustainability (B-Leaders) project focused on increasing the resiliency of the power sector to the environmental stresses of economic growth and established a working model for the use of renewable energy resources—essentially decoupling economic growth in the Philippines from increased greenhouse gas emissions.

A project that promoted borad-based economic growth and financial inclusion by significantly increasing the use of digital payments in the Philippines. Through the E-PESO project, USAID contributed to the Philippine government’s achievement of increasing e-payments usage from one percent in 2015 to 11 percent by the end of 2018.

This project fostered the development of conditions for broad-based, inclusive and resilient economic growth of cities and surrounding areas outside of Metro Manila. SURGE assisted cities and adjacent areas to plan effectively, guarantee basic public services, reduce business transaction costs, promote competitiveness, support sustainable development, and reduce disaster and climate change risks while insuring inclusive and sustainable growth.

Municipal Waste Recycling Project
USAID received a Congressional Directive in 2015 to support increased recycling of waste that threatens human health and the environment. As a part of this objective, USAID launched the Municipal Waste Recycling Project, which provided grants and technical assistance to waste recycling programs, with a particular focus on improving waste management practices and reducing plastics pollution in marine environments.

Toxic Site Identification Program
Beginning in 2017, with the support of USAID, Pure Earth piloted a more comprehensive investigative assessment approach to evaluating Iloilo City and Tagbilaran City, collecting over 19,000 samples in 95 randomly selected barangays. The intent of the more extensive approach was to evaluate heavy metals concentrations across the cities in an effort to understand the geographic distribution of heavy metals in soil and to potentially identify sites for more targeted investigations.
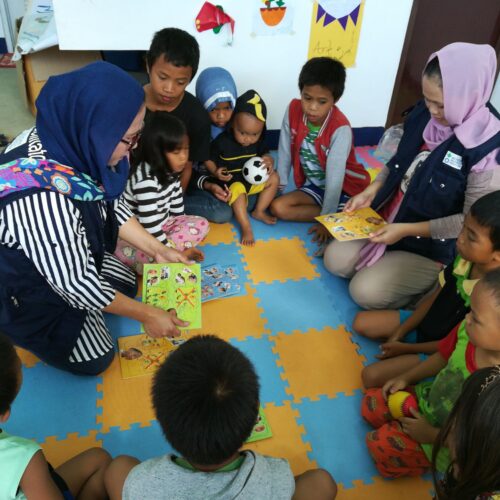

The project is designed to improve economic conditions and strengthen community cohesion among displaced persons and their host communities in Marawi and neighboring areas after the conflict in the region in 2017.
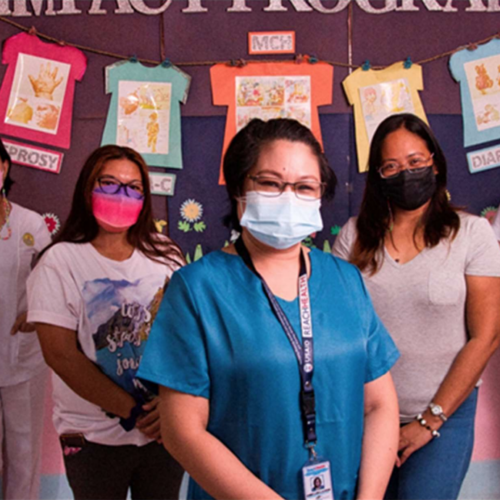

Climate stressors place additional pressure on the Philippines’ health sector because they can create sudden, overwhelming demand for services as they damage physical infrastructure and disrupt access to care. To address these challenges, USAID ReachHealth integrated climate risk management into the design, implementation, and sustainability of its family planning, maternal and neonatal health services to women and adolescent girls.
2019 Urban Milestone
The Department of Human Settlements and Urban Development Act of 2019 defined the new urban development and housing agency’s mandate, powers and functions, and appropriating funds.
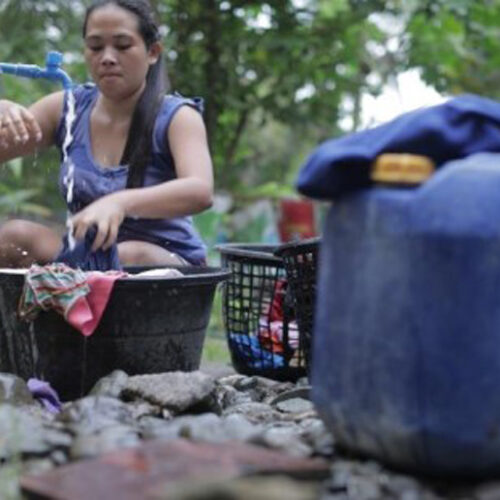

This project improves water security for water stressed communities in Palawan, Negros Occidental and Sarangani provinces. It works to increase access to resilient water supply and sanitation services, improve the sustainable management of water resources, and strengthen water sector governance. This initiative provides local government units, water service providers, and watershed councils in target provinces with the information, incentives, and partnerships they require to identify and address barriers to a water-secure future.
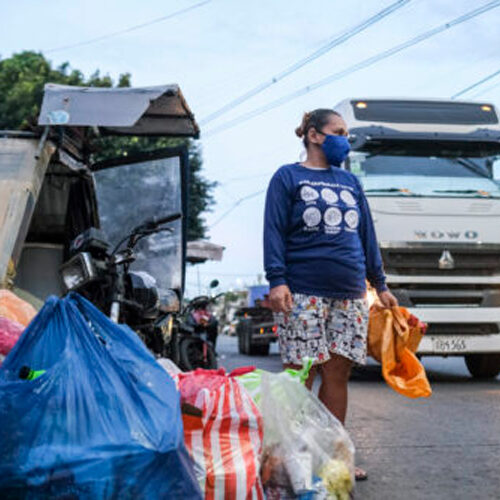

USAID launched CCBO as its flagship program to respond to the ocean plastic pollution crisis. The program works at the global level and in specific countries like the Philippines to address ocean plastics directly at their source.
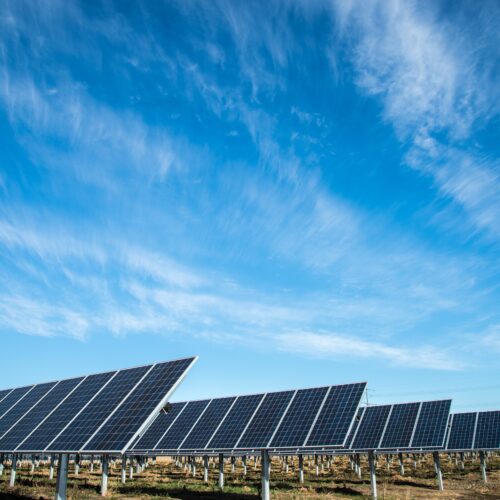

This project promotes the country’s key energy sector priorities and supports its climate mitigation goals to support a more competitive, secure, and resilient Philippine energy sector. Through the Energy Secure Philippines Project, the U.S. will work with the Philippine government and private sector partners to improve the performance and efficiency of energy utilities, deploy renewable energy systems, enhance competition in the power sector, and address energy sector cybersecurity.
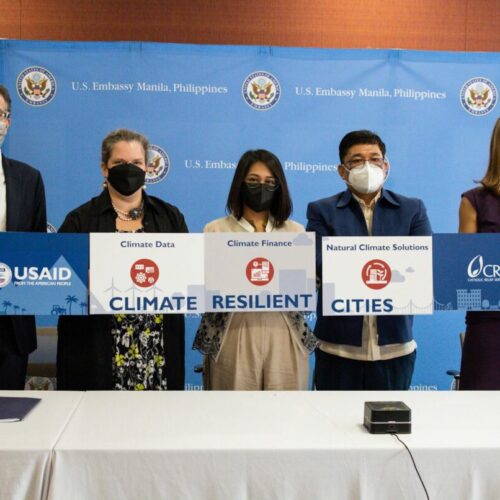

USAID is helping Philippine cities adapt to, mitigate, and endure the impacts of climate change by increasing their access to climate financing and tools to build resilience. Through this project, the U.S. government will support local government units and other stakeholders to better understand, use, and disseminate climate information to local communities.

Cities for Enhanced Governance and Engagement
This is a five-year project that supports the practice of good local governance in the Philippines through three objectives, namely: (1) strengthen enabling environment for decentralization; (2) enhance service delivery capacity, legitimacy, transparency, and accountability of participating local governments; and (3) empower citizens by increasing participation in and oversight of local governance processes. CHANGE is an integral component of the Mission’s Cities Development Initiative (CDI) and is implemented in the cities of Batangas, Legazpi, Puerto Princesa, Iloilo, Tagbilaran, Cagayan de Oro, Zamboanga, General Santos, and Tacloban.
2022 Urban Milestone
The Extended Producer Responsibility on Plastic Packaging Waste was lapsed into law in 2022, amending the Ecological Solid Waste Management Act of 2000.

